Difference between revisions of "Displays"
(Some edits, add info for 15kHz output and transcoders) |
|||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
*Wii would be the easiest method. Can output to 240p. | *Wii would be the easiest method. Can output to 240p. | ||
| − | *VGA to | + | *VGA to Composite/S-Video converter box. These are cheap but only output 480i and may introduce latency, and may have poor picture quality compared to the actual console's Composite/S-Video output. |
| + | |||
| + | *Driver modifications like [http://wiki.arcadecontrols.com/wiki/Soft-15khz Soft15khz] and [[GroovyMAME|CRT_Emudriver]] can allow your video card to output real 15kHz RGB through the VGA/DVI port. May need to buy or create your own specialized cables depending on the CRT you use. For CRT's that don't have RGB inputs, you can use a VGA/RGB to YPbPr transcoder (such as the [http://www.curtpalme.com/TC1500.shtm Crescendo TC1500]) to change the signal type to YPbPr component video without any scaling or latency. | ||
*Most CRT HDTVs have either DVI or HDMI ports which can accept as low as 30kHz (480p at 60Hz) from a PC | *Most CRT HDTVs have either DVI or HDMI ports which can accept as low as 30kHz (480p at 60Hz) from a PC | ||
| Line 111: | Line 113: | ||
==External Links== | ==External Links== | ||
| − | [http://retrorgb.com RetroRGB] - Provides lots of info on displays<br> | + | *[http://retrorgb.com RetroRGB] - Provides lots of info on displays<br> |
| − | [http://junkerhq.net/xrgb/index.php/240p_test_suite 240p test suite] - Test suite for properly configuring 240p. Designed mostly for CRTs, but will work with any monitor that supports 240p. Available as a homebrew program for several consoles. | + | *[http://junkerhq.net/xrgb/index.php/240p_test_suite 240p test suite] - Test suite for properly configuring 240p. Designed mostly for CRTs, but will work with any monitor that supports 240p. Available as a homebrew program for several consoles. |
[[Category:FAQs]] | [[Category:FAQs]] | ||
[[Category:Recommendations]] | [[Category:Recommendations]] | ||
Revision as of 00:13, 27 November 2014
There are several displays you can use for emulation. Some are better than others at displaying older standard definition games.
This FAQ is very work in progress. Please expand upon it.
Contents
CRT TVs
- Main article: CRT TVs
They come in several forms:
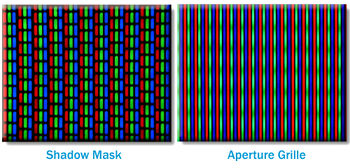
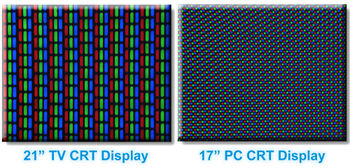
- Shadow Mask
- Aperture grille
- HD CRTs
Features:
- Can display a wide range of resolutions up to 480i on SDTVs and 1080i on HDTVs
- May actually force and scale to a resolution non-native to the input. HDTVs that scale EVERYTHING to 1080i aren't rare. That defeats the purpose of avoiding scaling, but you still get the other benefits.
- No input delay
- Very fast response times
- True black levels
- Wide viewing angles
- 4:3 Aspect ratio (with a few exceptions)
How to connect to a CRT TV:
- Wii would be the easiest method. Can output to 240p.
- VGA to Composite/S-Video converter box. These are cheap but only output 480i and may introduce latency, and may have poor picture quality compared to the actual console's Composite/S-Video output.
- Driver modifications like Soft15khz and CRT_Emudriver can allow your video card to output real 15kHz RGB through the VGA/DVI port. May need to buy or create your own specialized cables depending on the CRT you use. For CRT's that don't have RGB inputs, you can use a VGA/RGB to YPbPr transcoder (such as the Crescendo TC1500) to change the signal type to YPbPr component video without any scaling or latency.
- Most CRT HDTVs have either DVI or HDMI ports which can accept as low as 30kHz (480p at 60Hz) from a PC
- They do not support 120Hz to force 240p resolutions while doing this[citation needed]
CRT monitors
- All the benefits of a CRT TV besides native inputs for actual hardware
- Generally 30kHz (480p at 60Hz) horizontal frequency at minimum, unless the monitor is tri-sync (15kHz, 25kHz, 31kHz).
- You can force 240p resolutions with 120Hz refresh rates. You can then use black frame insertion to get the effective refresh rate back down to 60hz.
- There are also hacks, both software and hardware, to allow 15kHz output. But the monitor must also support it, and most of them aren't written for modern OSs. Careful there.
- Larger resolutions available, often massive
- Horizontal resolution is only limited by video bandwidth, so you can set it really high and scale output to fit, and the CRT will display it 4:3. This is useful for 240p modes where you can avoid having to have different custom resolutions for each game and not have any visible scaling issues due to individual horizontal pixels being smaller than your monitor's dot pitch.
- Large range of vertical refresh rates supported, often 50Hz to 160Hz. It's possible to display arcade games like R-Type and others with unusual refresh rates almost exactly the same as the real cabinet did, with perfect smooth scrolling. V-sync is still needed due to dot clock granularity and the fact the emulator frames needs to be synchronized to the CRT's vertical retrace, otherwise you will get some minor static tearing.
- Keep in mind your vertical refresh rate and vertical resolution must stay within your monitor's horizontal frequency limits, e.g. if your monitor's limits are 30kHz to 70kHz and you are trying to set a display mode for PAL games, you will find that 480p at 50Hz is not possible as that is 25kHz, you will need to increase the vertical resolution to around 576p to make it 30kHz.
- Easy to connect to a computer
- Not as large as many TVs, rarely larger than 19" or 21"
- 4:3 Aspect ratio (with a few exceptions, notably the FW900)
240p/480i Emulation on a 31kHz CRT Monitor
Given the many advantages that CRT monitors possess, they make ideal displays for emulation, particularly for 5th-gen games and below. However, to get the most out of them, some extra steps may be necessary. For instance, some games used interlaced modes, which without a shader results in ugly deinterlacing artifacts. Also, even at 480p, games that ran at 240p and below look blocky and pixellated, not to mention correcting the aspect ratio for games using non-square pixels results in scaling artifacts, just as on an LCD. The scaling issues can be dealt with using a superwide 240p resolution, but that requires using 120hz with black frame insertion, and games that use 480i get downsampled to 240p, making it a less than ideal solution in those cases, although it does have lower latency due lower frame times between vsync.
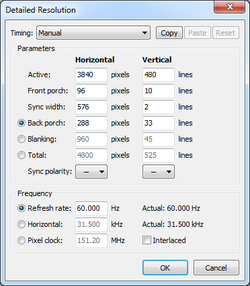
To correctly display games that need both 240p and 480i resolutions, the solution lies in creating a custom superwide 3840x480 modeline, combining it with a shader that scanlines 240p content and interlaces 480i content, and using both through RetroArch, essentially turning your monitor into an extremely sharp CRT TV. On Nvidia cards, the custom modeline can easily be set within your graphics card's drivers. On AMD, it requires the use of third-party software, such as Custom Resolution Utility. Simply add a detailed resolution with the exact settings shown on the picture, restart your computer, and the monitor should now be able to make use of the new modeline. As for the shader, hunterk's interlacing.cg gives you black lines that will oscillate when given an image with 400 or higher vertical resolution, emulating the behavior of 15kHz displays. There are also some shader presets that combine the interlacing shader with tvout-tweaks and image-adjustment for accurate RGB signal emulation and color controls, and also some that utilize Themaister's NTSC shader for composite/s-video emulation.
Once you have the new modeline set and have the shader in hand, open your RetroArch configuration file of choice, set the fullscreen resolution to 3840x480, aspect ratio to 8, and windowed fullscreen to false. Adjust your monitor's image as necessary. It may be necessary to raise your monitor's brightness somewhat, or increase color intensity to deal with the loss of brightness from having pure black scanlines. Some monitors, such as the NEC/Mitsubishi SuperBright series, have settings that increase the monitor's brightness without compromising black level or color temperature significantly.
LCD
(TN) displays
- Native resolution which all output must scale to
- Fairly fast response times
- 120hz displays with hacks can display motion at the same level as a CRT TV. See: http://www.blurbusters.com and http://www.techngaming.com/home/guide/tips/updated-eliminate-motion-blur-while-gaming-with-nvidia-lightboost-r485
IPS displays
- Native resolution which all output must scale to
- Fairly long response times (may differ between panels)
- Vivid colors and contrast
- Good viewing angles
- Massive resolutions available.
- Korean monitors such as Qnix QX2710 can run at 120Hz
Black frame insertion
For 120hz monitors.
Simulates CRT flicker, which is necessary for the human eye to perceive fluid motion. Without it, the sample-and-hold method used by LCDs manifests as motion blur to our eyes. For LCDs, running at 120Hz with black frame insertion every other frame gives you 60Hz CRT motion quality on 60fps content. This is especially effective on strobe-backlight gaming monitors (e.g. NVIDIA LightBoost, EIZO Turbo240, BENQ XL2720Z Blur Reduction) that often only enable motion blur reduction backlight strobing only at 120 Hz.
For CRT monitors, they can use a 120Hz refresh rate to sync to 30kHz (240p) resolutions. However, 240p at 120Hz can create motion blur, due to having twice as many frames being drawn on screen and overlapping. The solution is to draw a black frame every other frame. At 120Hz that essentially brings it back down to proper 60Hz. The issues are that brightness is halved and any frame drops or synchronization issues are very noticeable, so
In RetroArch, there is an option for black frame insertion in the video options in the menu. This makes it draw an extra black frame for every frame and it succeeds in making the motion smooth at 120Hz. There is an option to set the vsync swap interval if you want to double frames instead. The "refresh rate" setting should be set to 60Hz (monitor refresh rate/2) for accurate dynamic rate control in these cases.
120Hz with software inserted black frames has less latency than doing so on the display's hardware. It also has less latency vs. displaying straight 60Hz due to the decreased frame times between vsync in emulators. It also doubles the performance requirements of an emulator to maintain vsync for the same reason, so keep that in mind.
Upscalers
http://scanlines.hazard-city.de/
External Links
- RetroRGB - Provides lots of info on displays
- 240p test suite - Test suite for properly configuring 240p. Designed mostly for CRTs, but will work with any monitor that supports 240p. Available as a homebrew program for several consoles.